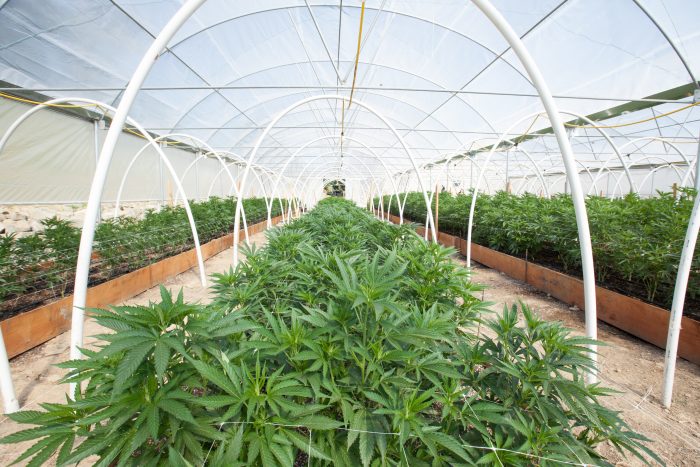
The Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs has issued new emergency rules to continue the implementation of the Medical Marihuana Facilities Licensing Act (MMFLA). These rules require “unlicensed operations of medical marihuana facilities to end on October 31, 2018”
Cannabis License Info
Information will be updated here as it becomes available. Check back for updates! Please note; while we aim to keep this pages fully up to date with the latest information, cannabis laws are always changing. We encourage you to verify these rules and regulations in the official legal text, which we’ve linked throughout the page for your convenience.
Medical Marihuana
Adult-Use/Recreational Marihuana
Michigan Seed-to-Sale Traceability Info
Michigan has created the Bureau of Medical Marihuana Regulation to centralize all aspects of medical marijuana regulation, the Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs reports. The new bureau is housed in Michigan’s Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs (LARA) and combines the existing oversight functions of the state’s patient and caregiver registry with the newly established statutory requirements for medical marijuana facility licensing.
Michigan has some unique nomenclature when it comes to their cannabis industry. Here are a few terms commonly used when discussing Michigan’s medical cannabis program that you should become familiar with:
- Marihuana – This is simply a different spelling of the more commonly used, Marijuana
- Provisioning Center – A dispensary where medical cannabis can be distributed and purchased by customers with a qualifying medical card
- Safety Compliance Facility – More commonly referred to as laboratories, these facilities are used for testing medical marihuana for potency and purity
Final Rules and Regulations related to Traceability. To view the complete rules please click here.
Rule 20. Transition period.
- (1) To ensure the safety, security, and integrity of the operation of marihuana facilities, there is a transition period consisting of 30 calendar days during which marihuana product can be entered into the statewide monitoring system to ensure statewide tracking beginning on the day a state operating license is issued to a licensee for the first time except for additional licenses issued to the same license holder for a stacked license after a first license is issued.
- (2) Within the 30-calendar-day period, a licensee shall do all of the following:
- (a) Record all marihuana product in the statewide monitoring system during this 30-calendar-day period as prescribed by the act and these rules.
- (b)Tag or package all inventory that has been identified in the statewide monitoring system as prescribed by the act and these rules.
- (c) Comply with all testing requirements as prescribed by the act and these rules.
- (3) After the 30-calendar-day period, any marihuana product that has not been identified in the statewide monitoring system under these rules and the act is prohibited from being onsite at a marihuana facility.
- (4) A violation of this rule may result in sanctions or fines, or both.
- (5) At any time during this 30-calendar-day period and thereafter, a marihuana facility is subject to an inspection under Rule 16.
Rule 24. Operation at a same location-grower, processor, and provisioning center.
- (1) Any combination of the following types of state operating licenses may operate as separate marihuana facilities at the same location:
- (a) A grower.
- (b) A processor.
- (c) A provisioning center.
- (2) To operate at a same location subject to subrule (1) of this rule all the following apply:
- (a) The department has authorized the proposed operation at the same location.
- (b) The operation at a same location shall not be in violation of any local ordinances or regulations.
- (c) The municipality shall not limit the type or number of marihuana facilities under section 205 of the act or prohibit the operation at the same location by local ordinance or zoning regulations.
- (d) Each marihuana facility subject to subrule (1) of this rule shall do all the following:
- (i) Apply for and be granted separate state operating licenses and pay a separate regulatory assessment for each state operating license.
- (ii) Have distinct and identifiable areas with designated structures that are contiguous and specific to the state operating license.
- (iii) Have separate entrances and exits, inventory, record keeping, and point of sale operations, if applicable.
- (iv) Post the state operating license on the wall in its distinct area and as provided in these rules.
- (e) Additional inspections and permits may be required for local or state building inspection, fire safety, and public health standards.
- (3) Operation of a state operating license at the same location that includes a licensed provisioning center shall have the entrance and exit to the licensed provisioning center marihuana facility and entire inventory physically separated from any of the other licensed marihuana facility or facilities so that persons can clearly identify the retail entrance and exit.
- (4) For purposes of this rule, a marihuana facility operating at a same location under this rule with multiple state operating licenses may transfer marihuana product or money between marihuana facilities authorized to operate at a same location under the following circumstances:
- (a) Each state operating license operating at a same location has common ownership.
- (b) An employee is designated by each licensee of a marihuana facility to monitor the transfer and execute the transfer or a licensed secure transporter executes the transfer in accordance with the act and these rules.
- (c) A manifest in the statewide monitoring system is created documenting the transfer as provided in the act and these rules.
- (d) Receipt of the transfer is recorded in the statewide monitoring system as provided in these rules.
Rule 29. Plant batches, testing procedures.
- (1) A grower shall uniquely identify each immature plant batch in the statewide monitoring system. Each immature plant batch must not consist of more than 100 immature plants.
- (2) A grower shall tag each plant that is greater than 8 inches in height or more than 8 inches in width with an individual plant tag and record the identification information in the statewide monitoring system.
- (3) A grower shall delineate or separate the plants as the plants go through different growth stages and ensure that the plant tag is always identified with the plant throughout the growth span so that all plants can be easily identified and inspected pursuant to the act and these rules. A grower shall ensure that identification information is recorded in the statewide monitoring system in accordance with the act, the marihuana tracking act, and these rules.
- (4) After a tagged plant is harvested, it is part of a harvest batch so that a sample of the harvest batch can be tested by a safety compliance facility. A grower shall isolate a harvest batch from other plants or batches that has test results pending. A harvest batch must be easily distinguishable from other harvest batches until the batch is broken down into packages.
- (5) Before the marihuana product can leave the grower facility, a sample of the harvest batch must be tested by a licensed safety compliance facility as provided in Rule 32, and test results must indicate a passed test result in the statewide monitoring system before the marihuana can be packaged. Marihuana product from harvest batches must not be transferred or sold until tested, packaged, and tagged as required under subrule (4) of this rule.
- (6) After test results show a passed test, the grower shall destroy the individual plant tags and the harvest batch is packaged. Each package must have a package tag attached. A grower shall ensure this information is placed in the statewide monitoring system in accordance with the act, the marihuana tracking act, and these rules.
- (7) A grower shall not transfer or sell any marihuana product that has not been packaged with a package tag attached and recorded in the statewide monitoring system in accordance with the act, the marihuana tracking act, and these rules.
- (8) After a processor receives or purchases a package in the statewide monitoring system, and the processor proceeds to process the marihuana product in accordance with the scope of a processor license, the act, and these rules, the processor must give the marihuana product a new package tag anytime it changes state or is incorporated into something else.
- (9) Once a package is created by a processor of the marihuana product in its final state, the processor shall have the sample tested pursuant to Rule 32. The processor shall not transfer or sell a final package until after test results indicate a passed test.
- (10) After a provisioning center receives or purchases marihuana product in the statewide monitoring system, a licensee may sell or transfer marihuana product only to a registered qualifying patient or registered primary caregiver under all of the following conditions:
- (a) The marihuana product has received passing test results in the statewide monitoring system. If the information cannot be confirmed, the marihuana product must be tested by a safety compliance facility and receive passing test results prior to sale or transfer.
- (b) The marihuana product bears the label required for retail sale under the act and these rules.
Rule 30. Retesting.
- (1) A safety compliance facility may test or retest a sample to validate the results of a failed quality assurance test except as indicated under subrule (2) of this rule. The marihuana facility that provided the sample is responsible for all costs involved in a retest.
- (2) A failed test sample must pass 2 separate retests consecutively in order to be eligible to proceed to sale or transfer. If both retests pass, then the batch is out of quarantine and eligible for sale or transfer. If 1 or both retests fail, then the marihuana product must be destroyed as provided in these rules.
- (3) Marihuana product is prohibited from being retested in all the following:
- (a) The marihuana product is in a final package.
- (b) An original test for pesticides failed pursuant to these rules. If the amount of pesticides is not permissible by the department, the marihuana product is ineligible for retesting and the product must be destroyed.
- (c) An original failed test for microbials on marihuana-infused product is ineligible for retesting and the product must be destroyed.
Rule 31. Testing; safety compliance facility.
- (1) A safety compliance facility shall use analytical testing methodologies for the required quality assurance tests in subrule (2) of this rule that are validated and may be monitored on an ongoing basis by the department or a third party which shall include either of the following:
- (a) Following the most current version of the Cannabis Inflorescence: Standards of Identity, Analysis, and Quality Control monograph published by the American Herbal Pharmacopoeia.
- (b) Following the alternative testing methodology approved by the department and validated by an independent third party that the methodology followed by the laboratory produces scientifically accurate results as quality assurance for each test it conducts.
- (2) A safety compliance facility shall conduct the required quality assurance tests that include all of the following:
- (a) Moisture content.
- (b) Potency analysis.
- (c) Tetrahydrocannabinol level.
- (d) Tetrahydrocannabinol acid level.
- (e) Cannabidiol and cannabidiol acid levels.
- (f) Foreign matter inspection.
- (g) Microbial and mycotoxin screening.
- (h) Pesticides.
- (i) Chemical residue.
- (j) Fungicides.
- (k) Insecticides.
- (l) Metals screening.
- (m) Residual solvents levels.
- (n) Terpene analysis.
- (o) Water activity content.
- (3) Except as otherwise provided, if a sample collected pursuant to Rule 32 or provided to a safety compliance facility pursuant to these rules does not pass the microbial, mycotoxin, heavy metal, pesticide chemical residue, or residual solvents levels test based on these rules, the marihuana facility that provided the sample shall dispose of the entire batch from which the sample was taken and document the disposal of the sample using the statewide monitoring system pursuant to the act, marihuana tracking act, and these rules.
- (4) For the purposes of the microbial test, a sample provided to a safety compliance facility pursuant to this rule is deemed to have passed if it satisfies the standards set forth in Table 9 of the Cannabis Inflorescence: Standards of Identity, Analysis, and Quality Control monograph adopted by reference pursuant to these rules.
- (5) For the purposes of the mycotoxin test, a sample provided to a safety compliance facility pursuant to this rule is deemed to have passed if it meets the following standards:
- (7) A safety compliance facility shall do the following:
- (a) Become fully accredited by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO/IEC 17025:2005, or by an entity approved by the department within 1 year after the date the license is issued and agree to have the inspections and reports of the International Organization for Standardization made available to the department.
- (b) Become provisionally accredited under subdivision (a) of this subrule within 6 months from the issuance of a license. A safety compliance facility may be ordered to cease operations if provisional accreditation is not received within 6 months.
- (a) Become fully accredited by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO/IEC 17025:2005, or by an entity approved by the department within 1 year after the date the license is issued and agree to have the inspections and reports of the International Organization for Standardization made available to the department.
- (c) Maintain internal standard operating procedures.
- (d) Maintain a quality control and quality assurance program.
- (8) The department shall establish a proficiency testing program and designate safety compliance facility participation. A safety compliance facility shall analyze proficiency test samples using the same procedures with the same number of replicate analyses, standards, testing analysts and equipment as used for marihuana product testing.
- (9) The department shall publish a list of approved pesticides for use in the cultivation and production of marihuana plants and marihuana products to be sold or transferred in accordance with the act or these rules. For the purposes of the pesticide chemical residue test, a sample provided to a safety compliance facility pursuant to this rule is deemed to have passed as to that chemical if the sample satisfies the most stringent acceptable standard for an approved pesticide chemical residue as set forth in Subpart C of 40 C.F.R. Part 180. 40 C.F.R., § 180, et seq. or FIFRA section 25(b), whichever is more stringent.
- (10) If a sample provided to a safety compliance facility pursuant to this rule and Rule 32 passes the tests required under subrule (2) of this rule, the safety compliance facility shall enter the information in the statewide monitoring system of passed test results. Passed test results must be in the statewide monitoring system for a batch to be released for immediate processing, packaging, and labeling for transfer or sale in accordance with the act and these rules.
- (11) A safety compliance facility shall enter the results into the statewide monitoring system and file with the department an electronic copy of each safety compliance facility test result for any batch that does not pass the required tests while it transmits those results to the facility that provided the sample. In addition, a safety compliance facility shall maintain the test results and make them available to the department upon request.
- (12) The department shall take immediate disciplinary action against any safety compliance facility that fails to comply with the provisions of this rule or falsifies records related to this rule, including any sanctions or fine, or both.
- (13) A safety compliance facility is prohibited from doing the following:
- (a) Desiccating samples.
- (b) Dry labeling samples.
- (c) Pre-testing samples.
- (14) A safety compliance facility shall comply with random quality assurance compliance checks upon the request of the department. The department or its authorized agents may collect a random sample of marihuana product from a safety compliance facility or designate another safety compliance facility to collect a random sample of marihuana product in a secure manner to test that sample for quality assurance compliance pursuant to this rule.
Rule 36. Marihuana product destruction and waste management.
- (1) Marihuana product that is to be destroyed or is considered waste must be rendered into an unusable and unrecognizable form and recorded in the statewide monitoring system.
- (2) A licensee shall not sell marihuana waste or marihuana products that are to be destroyed, or that the department orders destroyed.
- (3) A licensee shall manage all waste that is hazardous waste pursuant to part 111 of 1994 PA 451, MCL 324.11101 to 324.90106.
- (4) A licensee shall dispose of marihuana product waste in a secured waste receptacle using 1 or more of the following:
- (a) A manned and permitted solid waste landfill.
- (b) A manned compostable materials operation or facility.
- (c) An in-vessel digester.
- (d) In a manner in compliance with applicable state and local laws and regulations.
- (5) Wastewater generated during the cultivation of marihuana and processing of marihuana products shall be disposed of in compliance with applicable state and local laws and regulations.
Rule 35. Storage of marihuana product.
- (1) All inventory of marihuana products must be stored at a marihuana facility in a secured limited access area or restricted access area, and identified and tracked consistently with the statewide monitoring system under the act, the marihuana tracking act, or these rules.
- (2) All containers used to store marihuana products for transfer or sale between marihuana facilities must be clearly marked, labeled, or tagged, if applicable, and enclosed on all sides in secured containers. The secured containers must be latched or locked in a manner to keep all contents secured within. Each secured container must be identified and tracked in accordance with the act, the marihuana tracking act, and these rules.
- (3) All chemicals or solvents must be stored separately from marihuana products and kept in locked storage areas.
- (4) Marihuana-infused products or materials used in direct contact with such products must have separate storage areas from toxic or flammable materials.
- (5) A provisioning center shall store all marihuana products for transfer or sale behind a counter or other barrier separated from stock rooms.
- (6) A safety compliance facility shall establish an adequate chain of custody and instructions for sample and storage requirements.
- (7) A licensee shall ensure that any stock or storage room meets the security requirements of these rules and any other applicable requirements in the act and these rules.
Rule 33. Requirements and restrictions on marihuana-infused products; edible marijuana product.
- (1) A processor shall prepackage and properly label marihuana-infused products before sale or transfer.
- (2) A processor of marihuana-infused products shall list and record the THC level of marihuana-infused products, as provided in Rule 34, in the statewide monitoring system and indicate the THC level on the label along with the tag identification as required under these rules. Items that are part of a product recall issued in the statewide monitoring system, the department, or other state agency if applicable must be immediately pulled from production and not sold or transferred.
- (3) Marihuana-infused products must be stored and secured as prescribed under these rules.
- (4) At a minimum, a processor shall label any marihuana-infused product it produces or packages with all the following:
- (a) The name and address of the marihuana facility that processes or packages the marihuana-infused product.
- (b) The name of the marihuana-infused product.
- (c) The ingredients of the marihuana-infused product, in descending order of predominance by weight.
- (d) The net weight or net volume of the product.
- (e) For an edible marihuana product, the processor shall comply with subdivisions (a) to (d) of this subrule and all of the following:
- (i) Allergen labeling as specified by federal labeling requirements.
- (ii) If any nutritional claim is made, appropriate labeling as specified by federal labeling requirements and these rules.
- (iii) A statement printed in at least the equivalent of 11-point font size in a color that provides a clear contrast to the background: “Made in a marihuana facility.”
- (5) A processor of edible marihuana product shall comply with all the following to ensure safe preparation:
- (a) 21 CFR part 110, except that refrigerated potentially hazardous marihuana product must be stored at 4.4 degrees Celsius (40 degrees Fahrenheit) or below.
- (b) The licensee shall provide employee training on safe food handling by providing any of the following:
- (i) Proof of ServSafe certification.
- (ii) Documentation of employee training on food handling, including, but not limited to, allergens and proper sanitation and safe food handling techniques.
- (c) A licensee, to ensure the safe preparation standards under this subrule, shall comply with 1 or more of the following:
- (i) FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), 21 U.S.C. section 2201 et seq.
- (ii) Safe Quality Food (SQF), 7.2 edition.
- (iii)The International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO 22000/ISO/TS 22002-1.
- (d) The department may request in writing documentation to verify certifications and compliance with these rules.
- (6) A processor edible marihuana product must comply with all the following:
- (a) No edible marihuana product can be in a shape, color, package, or labeled in a manner that it would appeal to minors aged 17 years or younger. No edible marihuana product can be associated with or have cartoons, caricatures, toys, colors, designs, shapes, labels, or package that would appeal to minors.
- (b) No edible marihuana product can be easily confused with commercially sold candy. The use of the word candy or candies on the packaging or labeling is prohibited.
- (c) An edible marihuana product must be in child resistant packages or containers.
- (7) A processor is prohibited from producing an edible marihuana product that requires time or temperature control for safety. The end-product must be a stable shelf-life edible marihuana product.
- (8) For purposes of this rule, the term “edible marihuana product” means any marihuana-infused product containing marihuana that is intended for human consumption in a manner other than smoke inhalation.
- (9) This rule does not affect the application of any applicable local, state, or federal laws or regulations.
Rule 37. Tracking identification; labeling requirements; general.
- (1) All marihuana product sold or transferred between marihuana facilities must have the tracking identification number that is assigned by the statewide monitoring system affixed, tagged, or labeled and recorded, and any other information required by the department, the act, and these rules.
- (2) To ensure access to safe sources of marihuana product the department if alerted in the statewide monitoring system may recall any marihuana products, issue safety warnings, and require a marihuana facility to provide information material or notifications to a registered qualifying patient or registered primary caregiver at the point of sale.
Rule 38. Marihuana plant; tracking requirements.
Prior to a marihuana plant being sold or transferred, a package tag must be affixed to the plant or plant container and enclosed with a tamper proof seal that has the following information:
- (a) Business or trade name, licensee number, and RFID package tag assigned by the statewide monitoring system that is visible.
- (b) Name of the strain.
- (c) Date of harvest if applicable.
- (d) Seed strain if applicable.
- (e) Universal symbol if applicable.
Rule 39. Marihuana product sale or transfer; labeling requirements.
Prior to marihuana product being sold or transferred to or by a provisioning center, the container, bag, or product holding the marihuana product must have a label and be sealed with all the following information:
- (a) The name of the licensee and license number that is the producer, including business or trade name, and tag or source number as assigned by the statewide monitoring system.
- (b) The name of the licensee and license number including business or trade name of licensee that packaged the product, if different from the processor of the marihuana product.
- (c) The unique identification number for the package or the harvest if applicable.
- (d) Date of harvest.
- (e) Name of strain.
- (f) Net weight in United States customary and metric units.
- (g) Concentration of THC or CBD.
- (h) Activation time expressed in words or through a pictogram.
- (i) Name of the safety compliance facility that performed any test, any associated test batch number, and any test analysis date.
- (j) Universal symbol published by the department.
- (k) A warning that states all the following:
- (i) “For use by registered qualifying patients only. Keep out of reach of children.”
- (ii) “It is illegal to drive a motor vehicle while under the influence of marihuana.”
Rule 41. Daily purchasing limits; provisioning center.
The licensee shall verify in the statewide monitoring system before a sale or transfer of marihuana product to a registered qualifying patient or registered primary caregiver that the sale or transfer will not exceed the daily purchasing limit as follows:
- (a) For a registered qualifying patient, an amount of marihuana product that does not, in total, exceed 2.5 ounces per day.
- (b) For a registered primary caregiver, an amount of marihuana product that does not, in total, exceed 2.5 ounces per day for each registered qualifying patient with whom he or she is connected through the department’s registration process.
For the latest cannabis-related legislative updates on Michigan, check out our Cannabis Bill Tracker!